Climate change is one of the most pressing challenges of our time, and transitioning to renewable energy sources is a crucial step in mitigating its effects. Renewable energy offers a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels, which are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. Here’s a detailed look at how renewable energy plays a pivotal role in addressing climate change.
Benefits of Renewable Energy
- Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
Renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, produce little to no greenhouse gases during operation, significantly lowering carbon footprints.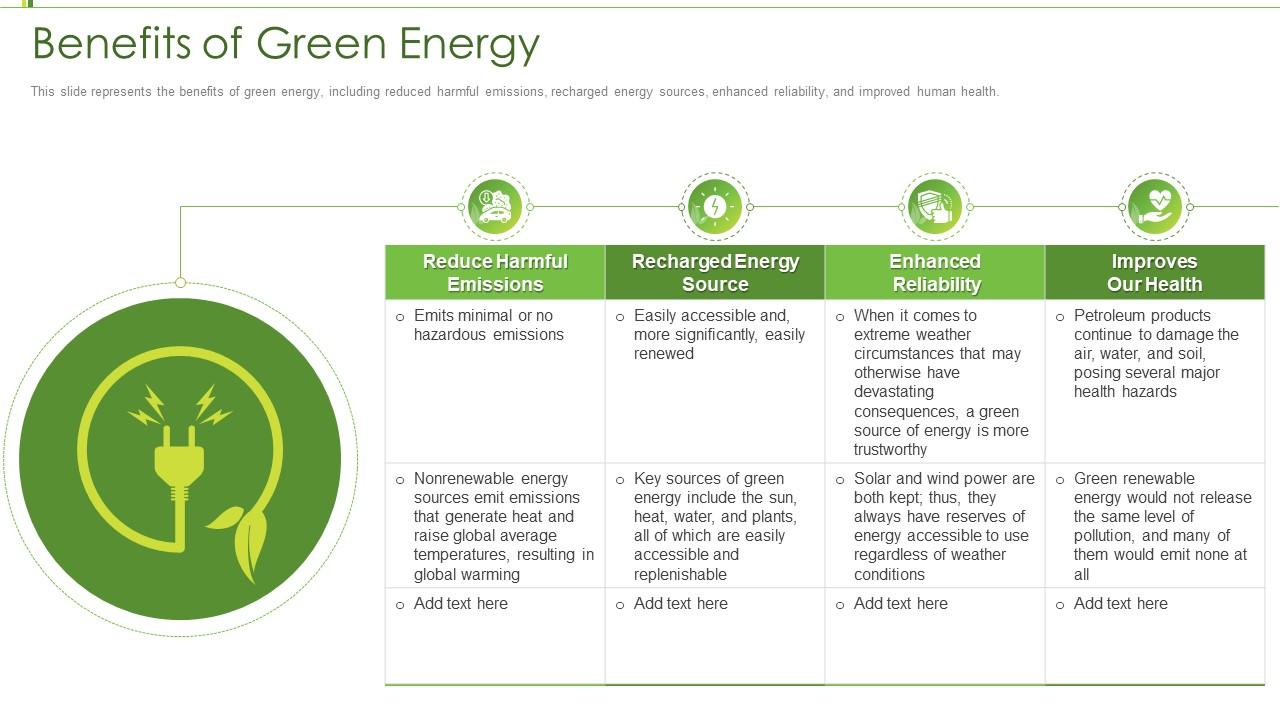
- Decreases Air Pollution:
Unlike fossil fuels, renewables do not release harmful pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, leading to improved air quality and public health. - Sustainable and Infinite Supply:
Renewable resources are abundant and inexhaustible, ensuring a continuous supply of energy without depleting natural resources.
Types of Renewable Energy Sources
- Solar Power
- Harnesses sunlight using photovoltaic cells or solar thermal systems.
- Scalable from small residential setups to large solar farms.
- Wind Energy
- Utilizes wind turbines to convert wind energy into electricity.
- Effective in both onshore and offshore locations.

- Hydropower
- Generates electricity by using flowing water to spin turbines.
- Can be implemented in various scales, from large dams to small run-of-the-river systems.
- Geothermal Energy
- Exploits the Earth’s internal heat for electricity generation and direct heating applications.
- Provides a constant and reliable energy source.
- Biomass Energy
- Converts organic materials, such as agricultural waste and wood, into energy.
- It can be used for electricity, heating, and as a biofuel.
Impact on Climate Change Mitigation
- Decarbonization of the Energy SectorTransitioning to renewables is essential for reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering overall carbon emissions.
- Promotes Energy IndependenceReduces dependence on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security and economic stability.
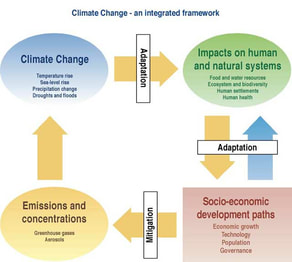
- Economic Growth and Job CreationThe renewable energy sector creates numerous jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, contributing to economic development.
- Technological AdvancementsContinuous innovation in renewable technologies leads to more efficient and cost-effective solutions, making renewables increasingly accessible.
Challenges and Solutions
- Intermittency Issues
- Renewables like solar and wind are weather-dependent, leading to potential intermittency.
- Solutions: Energy storage systems (e.g., batteries) and smart grids to balance supply and demand.

- Initial Costs
- High upfront costs for renewable energy infrastructure can be a barrier.
- Solutions: Government incentives, subsidies, and decreasing costs due to technological advancements.
- Infrastructure and Grid Integration
- Adapting existing grids to accommodate renewable energy sources can be complex.
- Solutions: Modernizing grid infrastructure and investing in smart grid technologies.
Global Initiatives and Policies
- International Agreements
- Paris Agreement: A global commitment to limit global warming and promote renewable energy.
- UN Sustainable Development Goals: Target affordable and clean energy for all.
- National PoliciesMany countries have implemented policies and incentives to promote renewable energy adoption, such as tax credits, feed-in tariffs, and renewable portfolio standards.
- Corporate CommitmentsNumerous companies are pledging to transition to 100% renewable energy, setting an example for sustainable business practices.
Conclusion
Renewable energy is a key component in the fight against climate change. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting sustainable development, and driving economic growth, renewables offer a viable path toward a cleaner, healthier, and more resilient future. Embracing renewable energy is not only an environmental imperative but also an opportunity for innovation and progress.

