The advent of 5G technology marks a significant milestone in the evolution of global telecommunications. As the fifth generation of wireless technology, 5G promises to revolutionize the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us. Its impact on the global economy is profound, paving the way for new opportunities and transforming various industries. Here’s a closer look at how 5G technology is shaping the global economy.
Enhanced Connectivity and Speed
- Faster Data Transmission: 5G offers speeds up to 100 times faster than 4G, enabling quick data transfer and reducing latency.
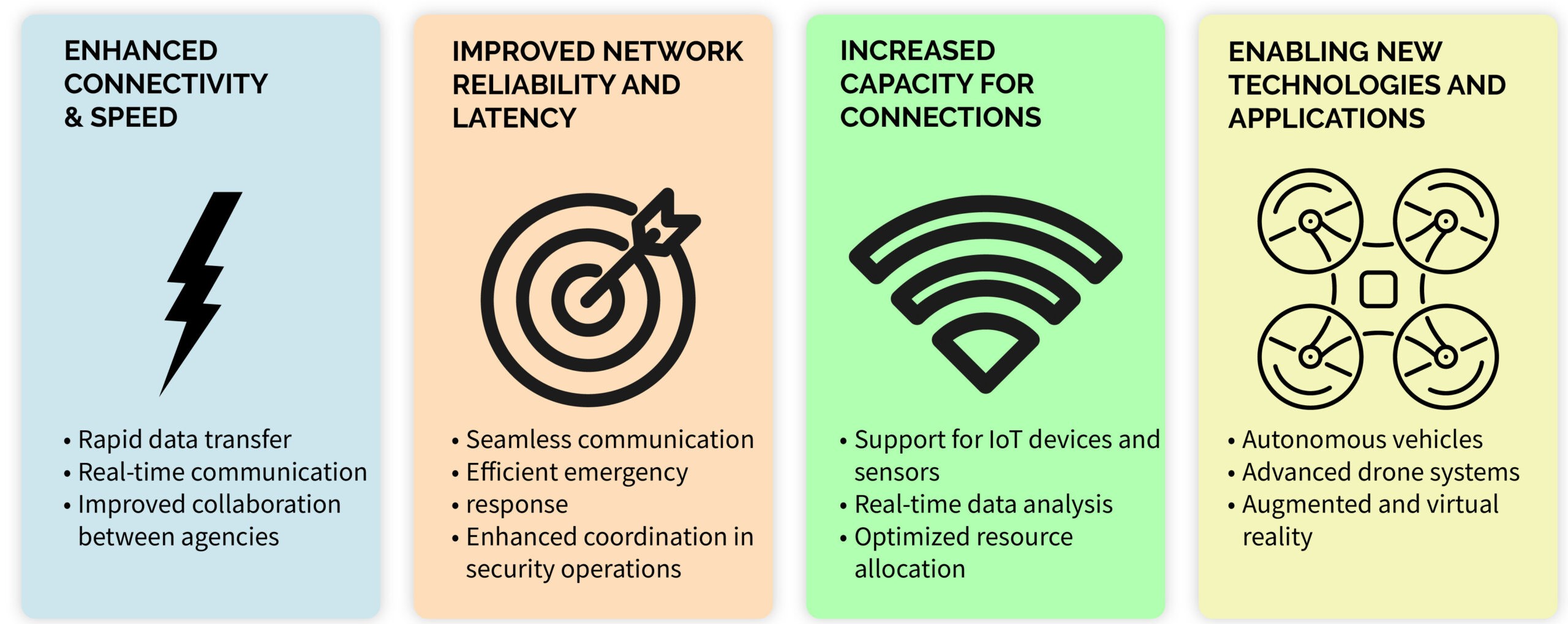
Advantages of 5g for Gov Inf - Improved Network Capacity: Enhanced capacity supports more connected devices simultaneously, facilitating the growth of IoT (Internet of Things).
- Reliable Communication: Increased reliability ensures seamless connectivity, crucial for critical applications like telemedicine and autonomous vehicles.
Transforming Industries
- Healthcare:
- Telemedicine: Enables real-time consultations and remote surgeries with high-quality video and low latency.
- Remote Monitoring: Improves patient care through continuous monitoring and data collection.
- Manufacturing:
- Smart Factories: Enhances automation and efficiency with real-time data and machine-to-machine communication.
- Predictive Maintenance: Reduces downtime by predicting and addressing equipment failures before they occur.
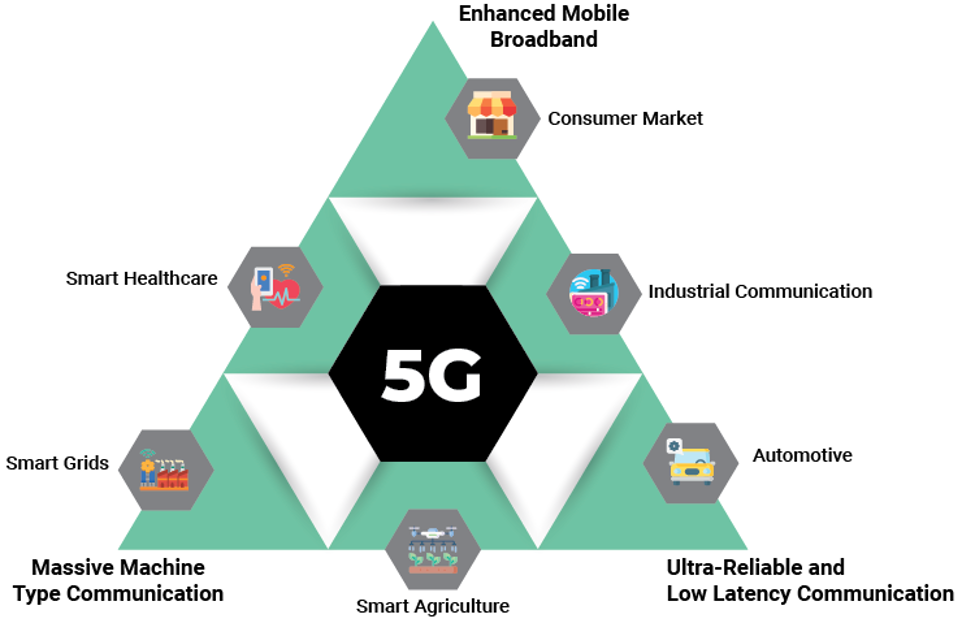
- Transportation:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Facilitates the development and deployment of self-driving cars with reliable, low-latency communication.
- Smart Traffic Management: Optimizes traffic flow and reduces congestion through real-time data analysis.
Driving Innovation and Economic Growth
- New Business Models: Encourages the creation of innovative business models and services, such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications.
- Job Creation: Generates new jobs in technology development, infrastructure deployment, and related sectors.
- Increased Productivity: Enhances productivity across industries by enabling faster decision-making and efficient operations.
Expanding Global Markets
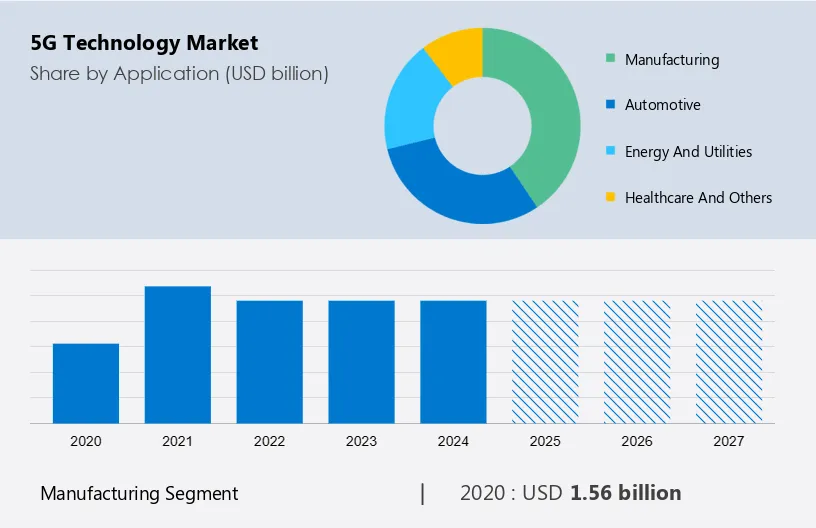
- Rural and Remote Connectivity: Extends high-speed internet access to underserved areas, promoting digital inclusion and economic development.
- Global Supply Chains: Improves supply chain management with real-time tracking and communication, increasing efficiency and reducing costs.
- Cross-Border Trade: Facilitates smoother international trade by streamlining logistics and enhancing communication between trading partners.
Enabling Smart Cities
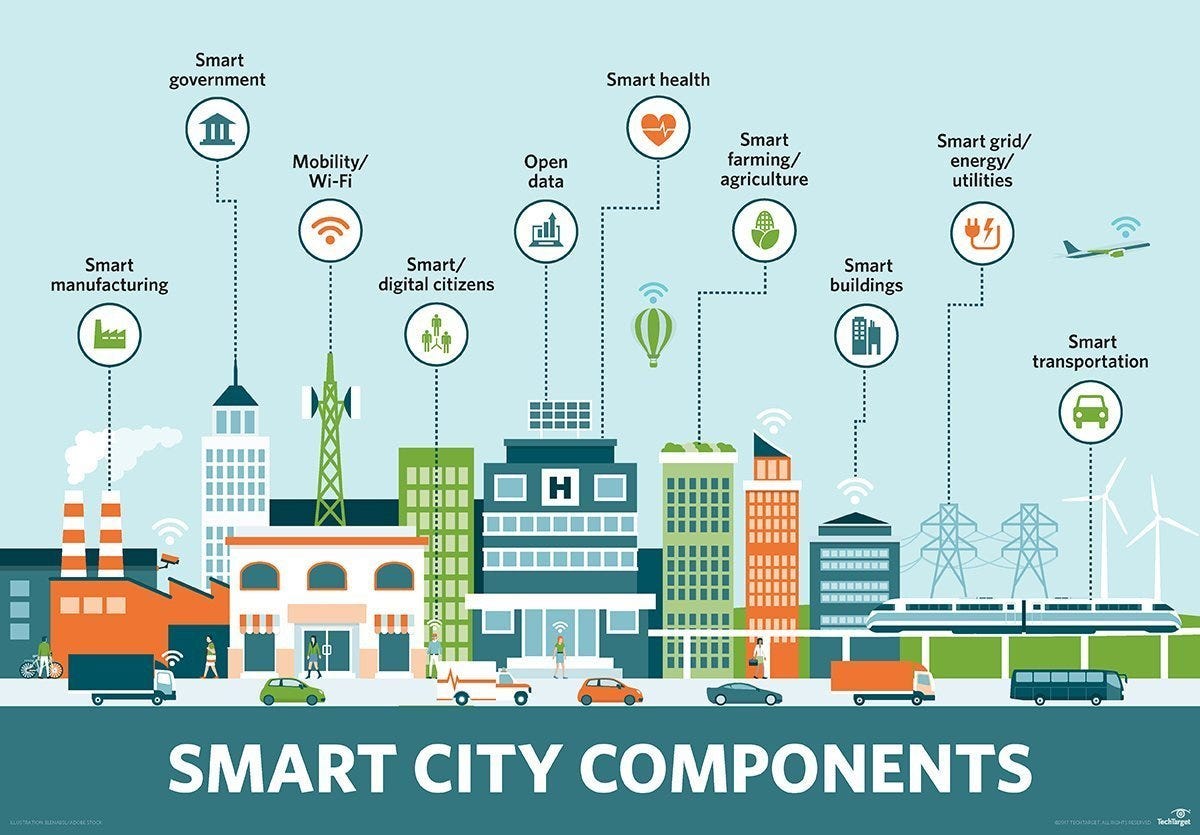
- Infrastructure: Supports the development of smart infrastructure, including intelligent transportation systems and energy-efficient buildings.
- Public Services: Enhances public safety and services with real-time monitoring and responsive systems.
- Environmental Sustainability: Promotes sustainability through efficient resource management and reduced emissions.
Overcoming Challenges
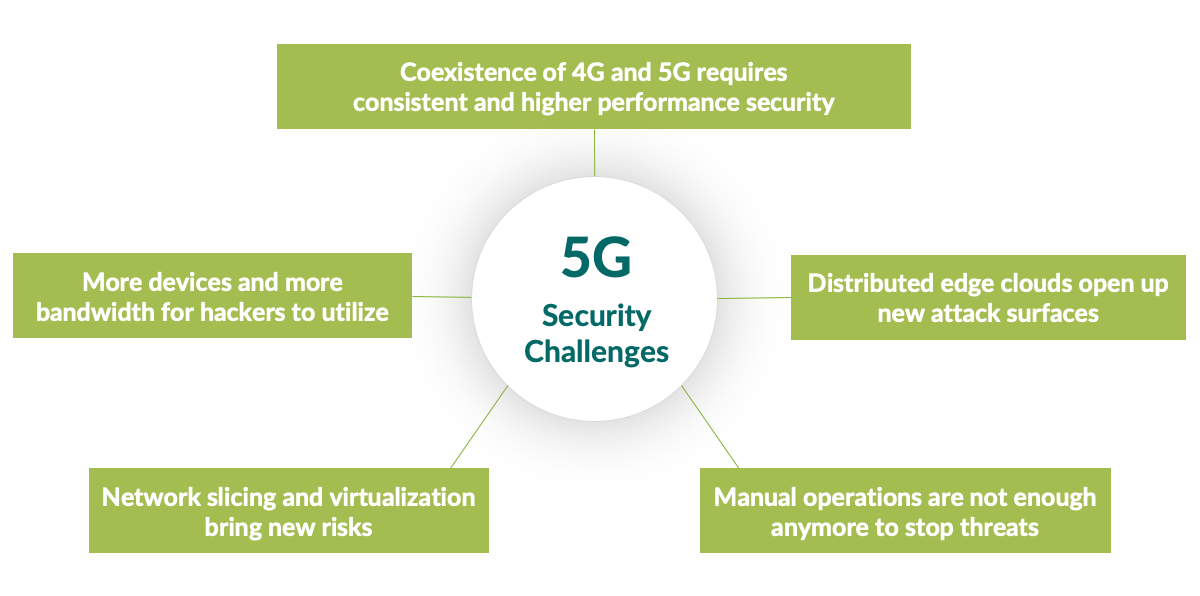
- Security Concerns: Addresses potential cybersecurity risks associated with increased connectivity and data transmission.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigates varying regulations and standards across different countries and regions.
- Infrastructure Investment: Requires significant investment in infrastructure development and upgrades to support widespread 5G deployment.
Conclusion
5G technology is not just an upgrade from its predecessors; it is a transformative force reshaping the global economy. By enhancing connectivity, driving innovation, and expanding markets, 5G is poised to unlock unprecedented economic opportunities and revolutionize various industries. As we continue to navigate the challenges and harness the potential of 5G, its impact on the global economy will only grow, paving the way for a more connected and prosperous future.

