 In an increasingly connected world, the demand for faster and more efficient data processing is driving significant advancements in technology. One such advancement is edge computing, which is transforming how data is processed and managed. Here’s a closer look at what edge computing is, its benefits, applications, and future potential.
In an increasingly connected world, the demand for faster and more efficient data processing is driving significant advancements in technology. One such advancement is edge computing, which is transforming how data is processed and managed. Here’s a closer look at what edge computing is, its benefits, applications, and future potential.
What is Edge Computing?
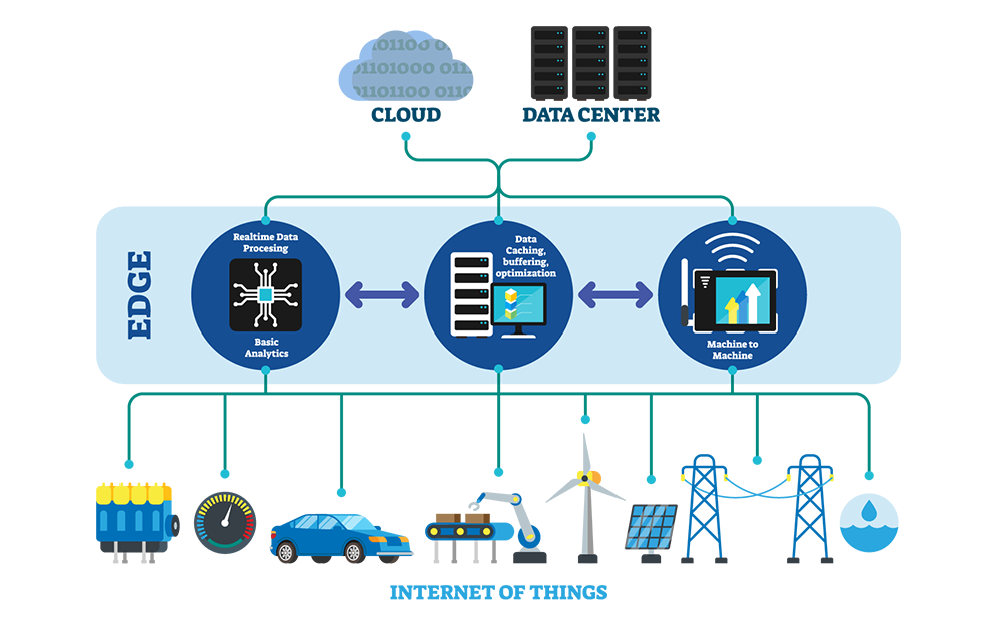
Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data near the edge of the network, close to the source of the data, rather than relying on centralized data centers. This approach reduces latency, conserves bandwidth, and enhances real-time data processing capabilities.
Benefits of Edge Computing
- Reduced LatencyProcessing data locally minimizes the time it takes to send data to a centralized cloud and back, enabling real-time decision-making and faster responses.
- Bandwidth EfficiencyBy handling data at the edge, only relevant information is sent to the cloud, reducing the amount of data transmitted and conserving bandwidth.
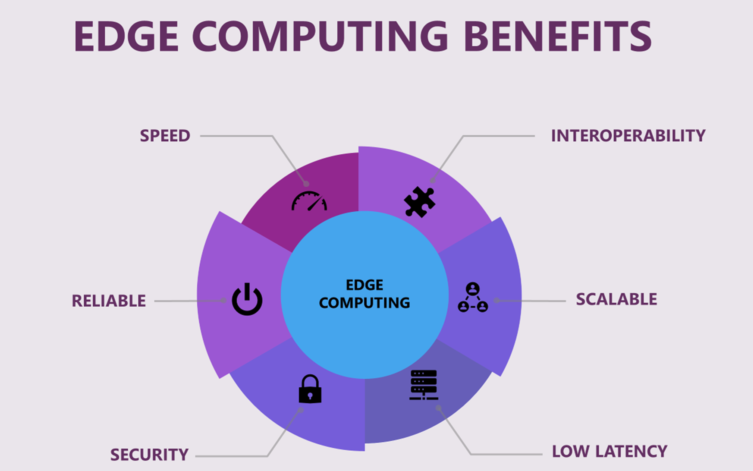
- Enhanced Privacy and SecurityKeeping data close to its source can improve security and privacy, as sensitive information doesn’t need to travel long distances or be stored in potentially vulnerable centralized systems.
- ScalabilityEdge computing allows for distributed processing power, making it easier to scale applications without overwhelming central servers.
Key Applications of Edge Computing
- Internet of Things (IoT)IoT devices generate vast amounts of data that need to be processed quickly. Edge computing enables real-time data analysis and action, making IoT applications more efficient and responsive.
- Autonomous VehiclesSelf-driving cars require immediate data processing for navigation and safety. Edge computing allows these vehicles to process data on-the-fly, improving their functionality and reliability.
- Smart CitiesEdge computing supports the infrastructure of smart cities by managing data from sensors and devices in real-time, optimizing traffic flow, energy usage, and public safety.
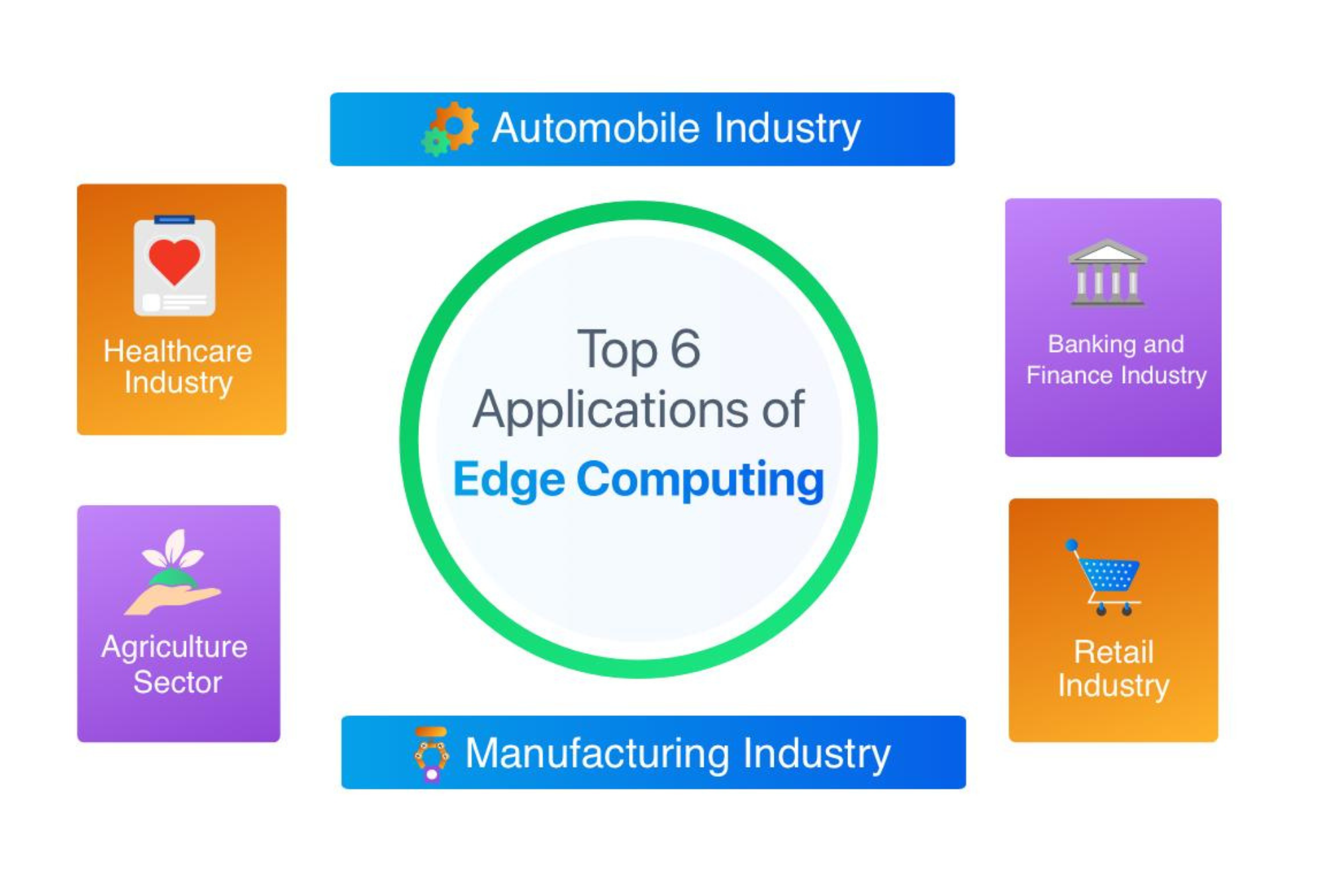
- HealthcareIn healthcare, edge computing facilitates real-time monitoring and analysis of patient data from wearable devices and medical equipment, enhancing patient care and outcomes.
- ManufacturingEdge computing in manufacturing allows for real-time monitoring and control of production lines, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
Challenges and Considerations
- Infrastructure InvestmentImplementing edge computing requires significant investment in local processing power and storage, which can be a barrier for some organizations.
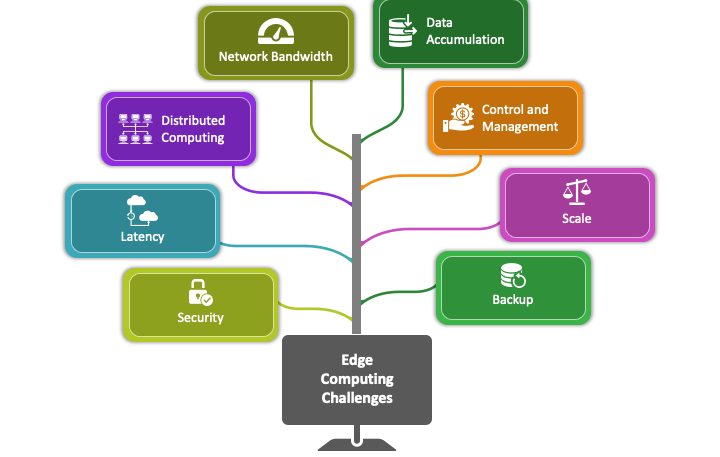
- Data ManagementManaging and orchestrating data across distributed edge devices can be complex, requiring sophisticated software and management tools.
- Security RisksWhile edge computing can enhance security, it also introduces new risks as more devices and endpoints are involved in the data processing chain.
The Future of Edge Computing
- 5G IntegrationThe rollout of 5G networks will further enhance the capabilities of edge computing by providing faster and more reliable connectivity, making real-time processing even more efficient.
- AI and Machine LearningIntegrating AI and machine learning at the edge will enable more advanced data processing and decision-making, leading to smarter and more autonomous systems.

- Increased AdoptionAs the benefits of edge computing become more apparent, its adoption is expected to grow across various industries, driving further innovation and development.
Conclusion
Edge computing is revolutionizing data processing by bringing computation closer to the data source. Its ability to reduce latency, conserve bandwidth, and enhance real-time processing makes it a crucial technology for the future. As industries continue to adopt and integrate edge computing, we can expect to see significant advancements in efficiency, security, and scalability.