Understanding Regulatory Compliance: A Key to Business Success

Introduction to Regulatory Compliance
- Definition: Adhering to laws, regulations, guidelines, and specifications relevant to business operations.
- Importance: Ensures legal and ethical standards are met, preventing legal penalties and enhancing reputation.
Types of Regulatory Compliance
- Financial Compliance: Adherence to financial reporting standards (e.g., Sarbanes-Oxley Act, IFRS).
- Data Protection Compliance: Ensuring data privacy and security (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
- Industry-Specific Compliance: Regulations tailored to specific sectors (e.g., HIPAA for healthcare, FDA regulations for pharmaceuticals).
Key Benefits of Regulatory Compliance
- Risk Mitigation: Reduces the risk of legal issues, fines, and reputational damage.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlines processes by establishing clear guidelines and
standards.
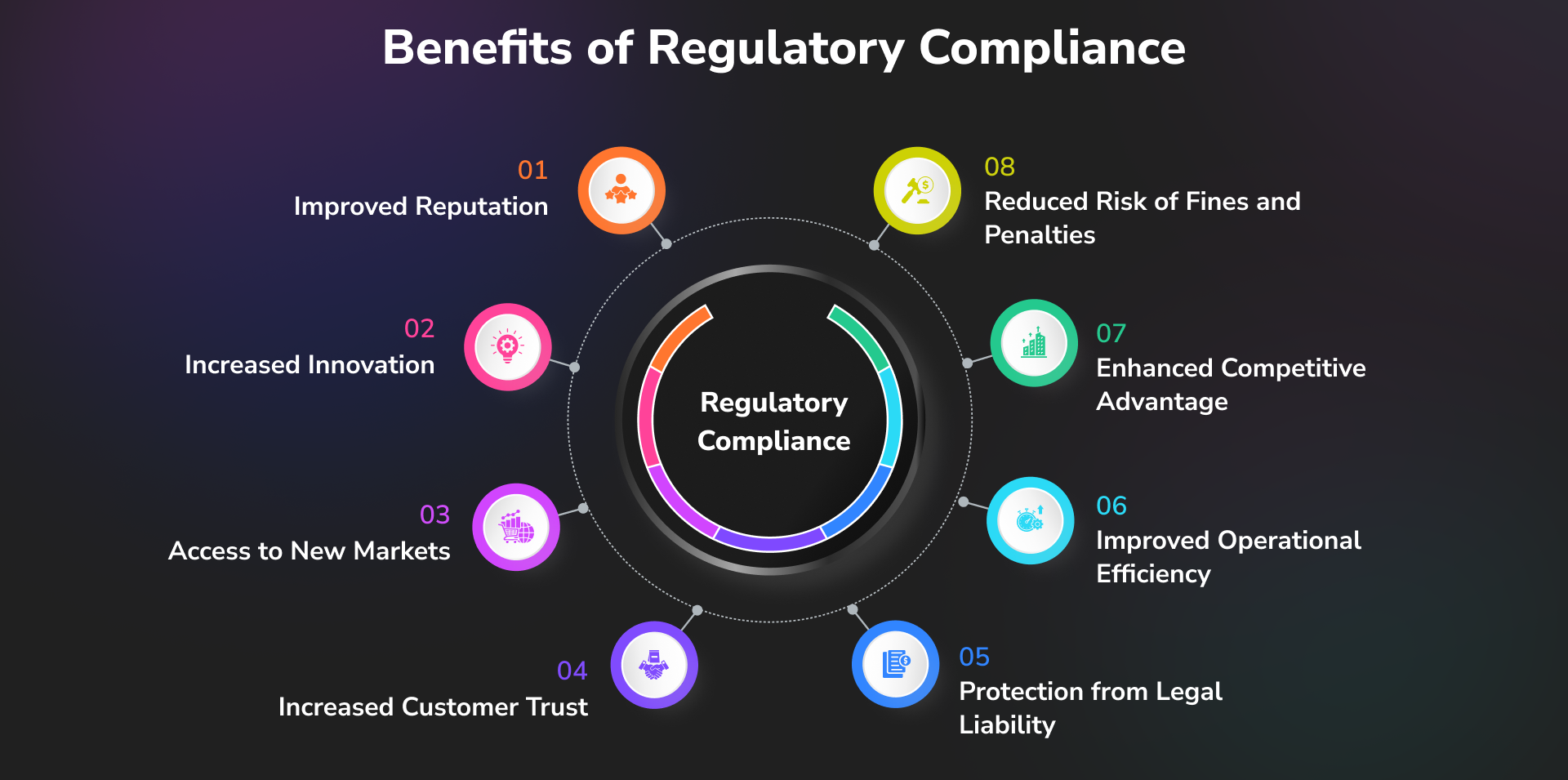
- Trust and Credibility: Enhances trust among customers, investors, and stakeholders by demonstrating a commitment to ethical practices.
Challenges in Maintaining Regulatory Compliance
- Complexity of Regulations: Navigating many local, national, and international regulations.
- Evolving Legal Landscape: Keeping up with frequent changes in laws and standards.

- Resource Allocation: Ensuring sufficient resources (time, money, personnel) are dedicated to compliance efforts.
Strategies for Effective Regulatory Compliance
- Regular Training: Conducting ongoing training programs for employees on compliance requirements and best practices.
- Compliance Audits: Performing regular audits to identify gaps and ensure regulation adherence.
- Technology Solutions: Leveraging compliance management software to automate monitoring and reporting processes.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Promoting cooperation among legal, finance, IT, and operational departments to ensure a holistic approach.
Case Studies: Success Stories
- Company A: Implemented a robust compliance management system, reducing regulatory breaches by 40%.
- Company B: Leveraged AI-powered tools to streamline compliance processes, resulting in a 30% increase in efficiency.
Future Trends in Regulatory Compliance
- Increased Scrutiny: Anticipate heightened regulatory scrutiny in data protection and environmental sustainability areas.
- Technological Advancements: Growing adoption of blockchain, AI, and machine learning to enhance compliance efforts.
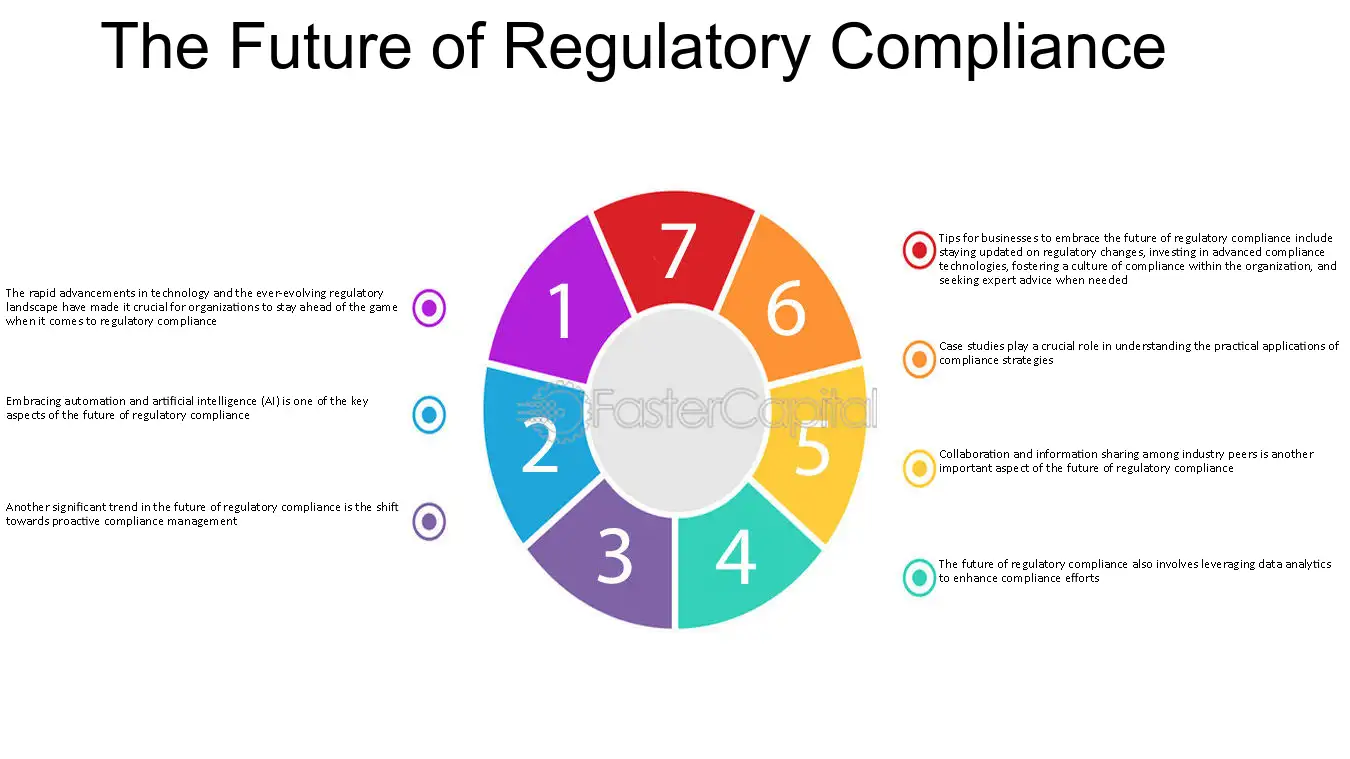
- Global Harmonization: Efforts towards standardizing regulations across borders to facilitate international business.
Conclusion
- Emphasize the critical role of regulatory compliance in safeguarding business interests.
- Encourage proactive measures and continuous improvement to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape effectively.





