In the domain of innovation, quantum computing stands as a signal of advancement, promising to revolutionize how we prepare data. This rising field mixes the standards of quantum mechanics with computational science, proclaiming a modern time of computing control and proficiency. To get a handle on the nuts and bolts of quantum computing, we must to begin with dig into its essential concepts and how they veer from classical computing.
The Quantum Bit: Qubit
What is Qubit?
At the heart of quantum computing lies the qubit, or quantum bit. Not at all like classical bits, which exist entirely as 0s or 1s, qubits saddle the unconventional properties of quantum mechanics, especially superposition and entanglement.
Superposition permits qubits to exist at the same time in numerous states. Envision a qubit as a turning coin: or maybe than being heads or tails, it can speak to both states at once. This capability exponentially increments the sum of data a quantum computer can handle compared to classical computers, which are constrained to twofold states.
Entanglement is another foundation of quantum computing. This marvel happens when two qubits gotten to be interconnected in such a way that the state of one right away impacts the state of the other, notwithstanding of the separate isolating them. This interconnecting can be utilized to perform complex calculations at phenomenal speeds.
Quantum: Entryways and Circuits
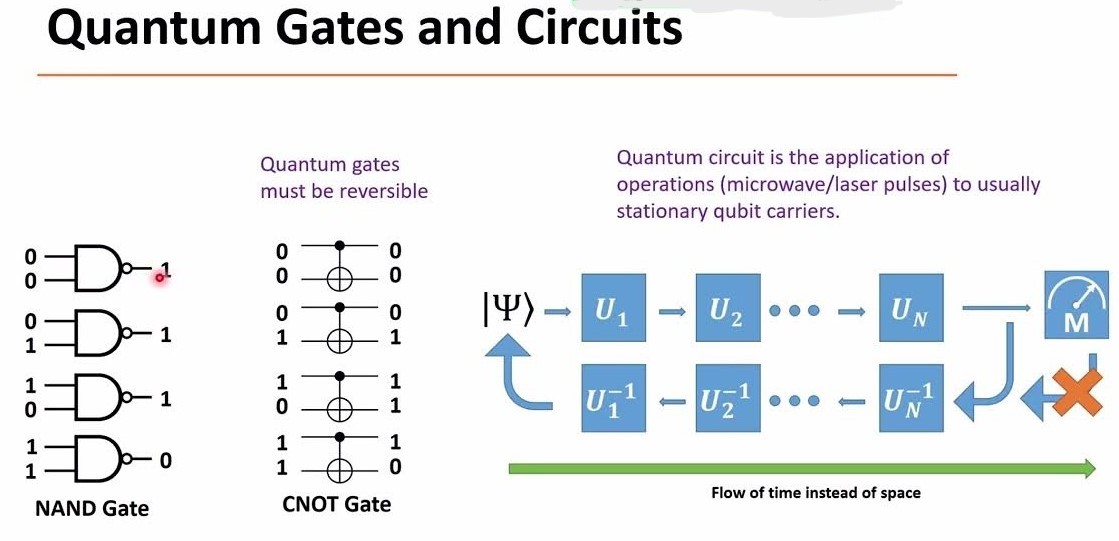
Building on the establishment of qubits, quantum entryways and circuits are the instruments by which quantum computers perform calculations. Quantum doors control qubits through operations practically equivalent to to classical rationale entryways, but they can perform distant more complex changes due to the standards of superposition and trap. An arrangement of these entryways shapes a quantum circuit, which executes a quantum algorithm.
Quantum: Algorithms
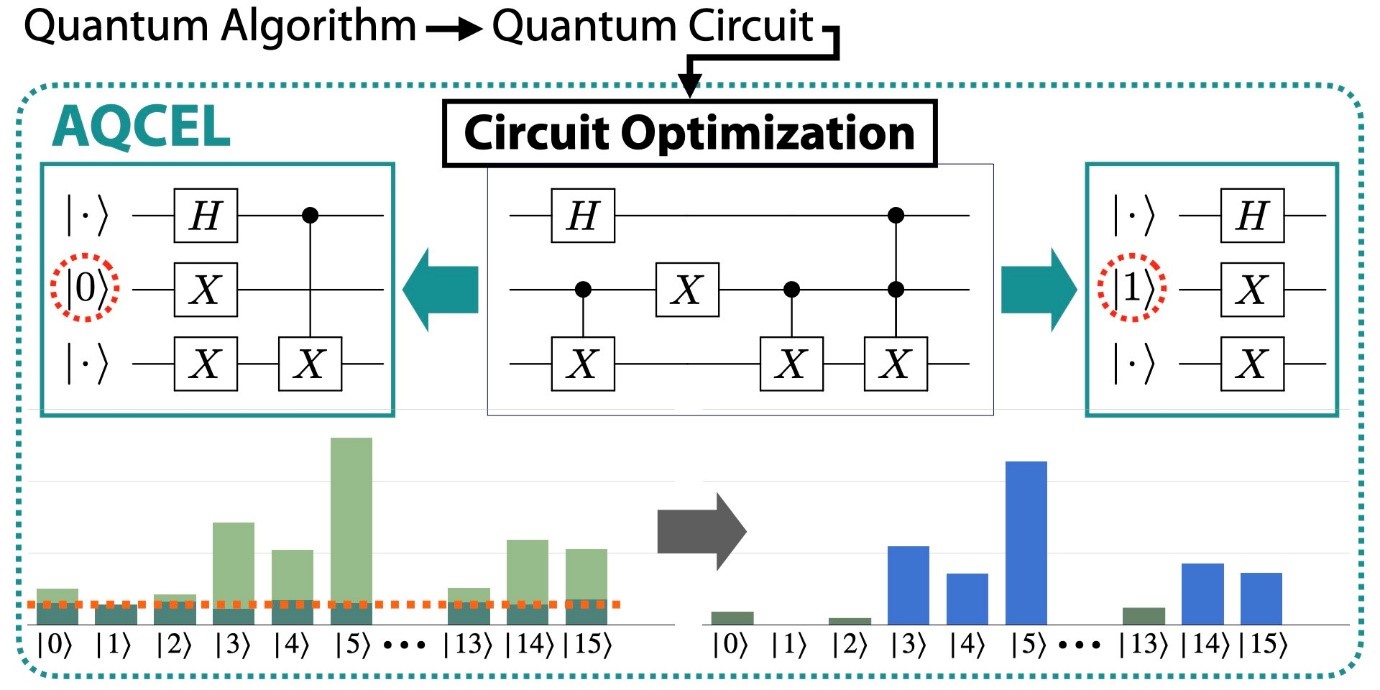
Quantum calculations are planned to abuse the interesting properties of quantum computing. One of the most popular is Shor’s calculation, which proficiently variables huge numbers, a errand that is famously challenging for classical computers. Another conspicuous case is Grover’s calculation, which quickens the look handle inside unsorted databases, giving a quadratic speedup over classical methods.
Quantum: Real-World Applications and Potential

The potential applications of quantum computing are tremendous and transformative. In cryptography, quantum computers might break numerous of the encryption frameworks right now in utilize, requiring the advancement of modern, quantum-resistant cryptographic strategies. In medication, quantum computing might lead to breakthroughs in medicate revelation and personalized treatment plans by recreating complex atomic intelligent more precisely than ever some time recently. Moreover, businesses such as fund, coordination, and fake insights stand to advantage from quantum-enhanced optimization and problem-solving capabilities.
Quantum: Challenges and Future Directions
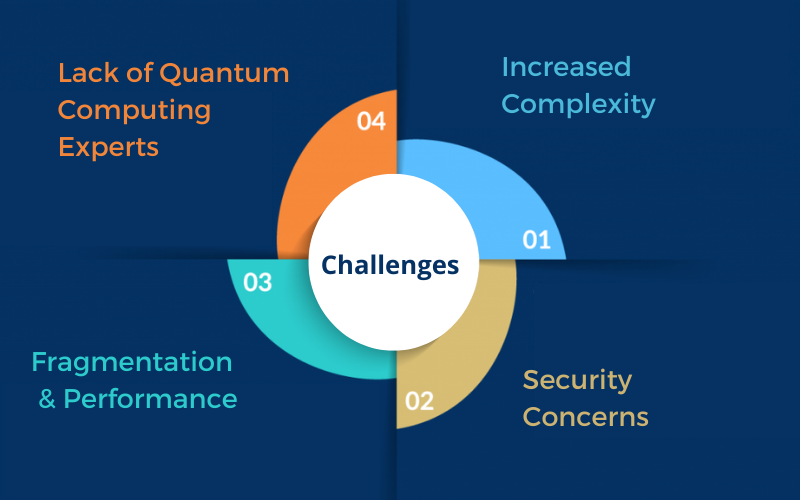
Despite its guarantee, quantum computing faces noteworthy specialized challenges. Qubits are exceedingly vulnerable to natural obstructions, driving to blunders in calculations. Creating steady and adaptable quantum frameworks requires modern mistake rectification strategies and propels in quantum hardware.
Moreover, the field is still in its earliest stages, with completely useful, large-scale quantum computers however to be realized. Be that as it may, considerable advance is being made by investigate teach and tech monsters alike, creeping us closer to down to earth quantum computing.
Conclusion:
Quantum computing speaks to a worldview move in how we approach computation. By leveraging the standards of superposition and trap, quantum computers can handle data in ways that classical computers cannot. As inquire about and advancement proceed to progress, the potential impacts of quantum computing on different segments seem be significant, proclaiming an unused period of mechanical innovation.

